Noticing blood coming from your mouth can be alarming. Many people experience bleeding while brushing, spitting, or even without any obvious reason. While the cause is often minor and related to oral health, in some cases it may indicate a more serious condition.
In this article, we explain why blood comes from the mouth, common reasons behind it, associated symptoms, treatment options, and when you should seek medical or dental help.
Blood in the mouth usually originates from the gums, teeth, tongue, throat, or oral tissues. The exact reason depends on factors such as oral hygiene, infections, injuries, medications, or underlying health conditions.
Understanding the cause early helps prevent complications.
Below are the most common and medically recognized causes.
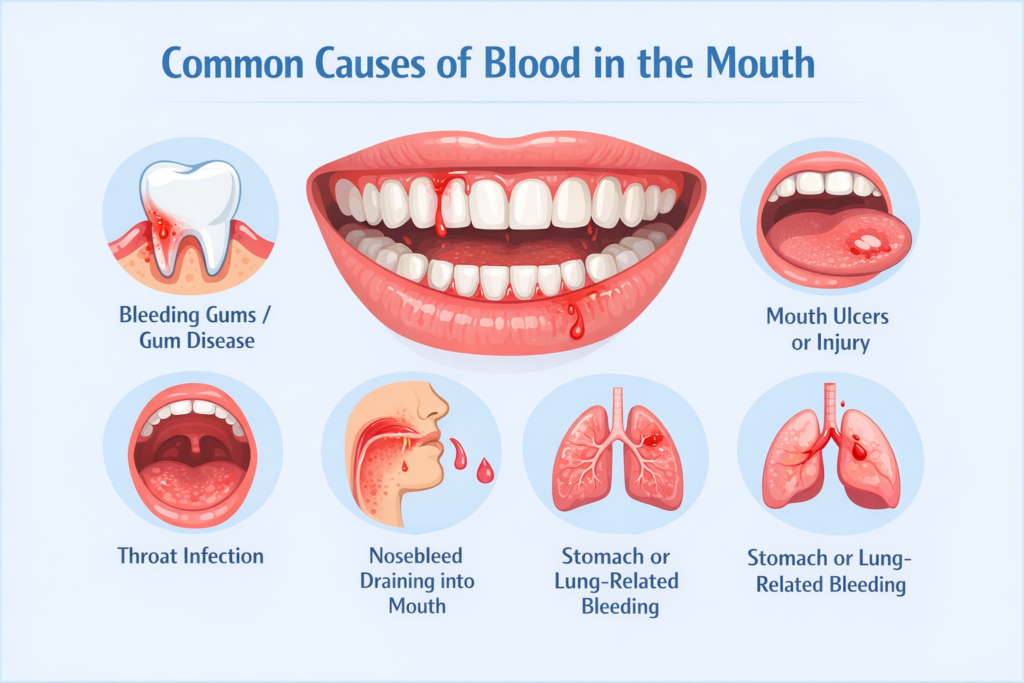
Gum disease is the leading reason for blood in the mouth.
Why it happens:
Plaque and tartar buildup
Bacterial infection of the gums
Inflammation (gingivitis)
Symptoms:
Bleeding while brushing or flossing
Red, swollen, or tender gums
Bad breath
Gum pain
If untreated, gum disease can progress to periodontitis, which may cause tooth loss.
Sometimes, bleeding is caused by mechanical injury rather than disease.
Common causes:
Aggressive brushing
Hard-bristled toothbrush
Incorrect flossing technique
This type of bleeding is usually mild and stops quickly after improving brushing habits.
Small wounds inside the mouth can bleed.
Causes include:
Mouth ulcers
Accidentally biting the cheek or tongue
Sharp tooth edges
Dental appliances
These injuries usually heal within 7–10 days.
A dental infection can explain why blood comes from the mouth, especially when accompanied by pain.
Symptoms:
Persistent toothache
Swelling near the tooth
Pus discharge
Bad taste in mouth
Bleeding near the infected area
This condition requires urgent dental treatment.
Many patients report seeing blood only in the morning.
Possible reasons:
Dry mouth during sleep
Mouth breathing
Early gum disease
Smoking or tobacco use
If this occurs regularly, a dental examination is recommended.
Certain medicines and health issues increase bleeding risk.
Examples:
Blood-thinning medications
Vitamin C or Vitamin K deficiency
Liver disorders
Blood clotting disorders
If bleeding occurs without dental causes, medical evaluation is important.
Tobacco irritates oral tissues and weakens gum health.
Effects:
Increased gum inflammation
Delayed healing
Higher risk of oral infections
Frequent bleeding
Quitting tobacco significantly improves oral and overall health.
In rare cases, blood from the mouth may indicate:
Oral cancer
Throat infections
Respiratory conditions
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Immediate medical attention is needed if bleeding is heavy, frequent, or unexplained.
Depending on the cause, you may notice additional symptoms.
Digestive System Symptoms
Abdominal pain or cramping
Vomiting blood
Dark or bloody stools
Respiratory Symptoms
Persistent coughing
Difficulty breathing or swallowing
Throat or neck swelling
General Warning Signs
Dizziness or fainting
Weakness or fatigue
Pale skin
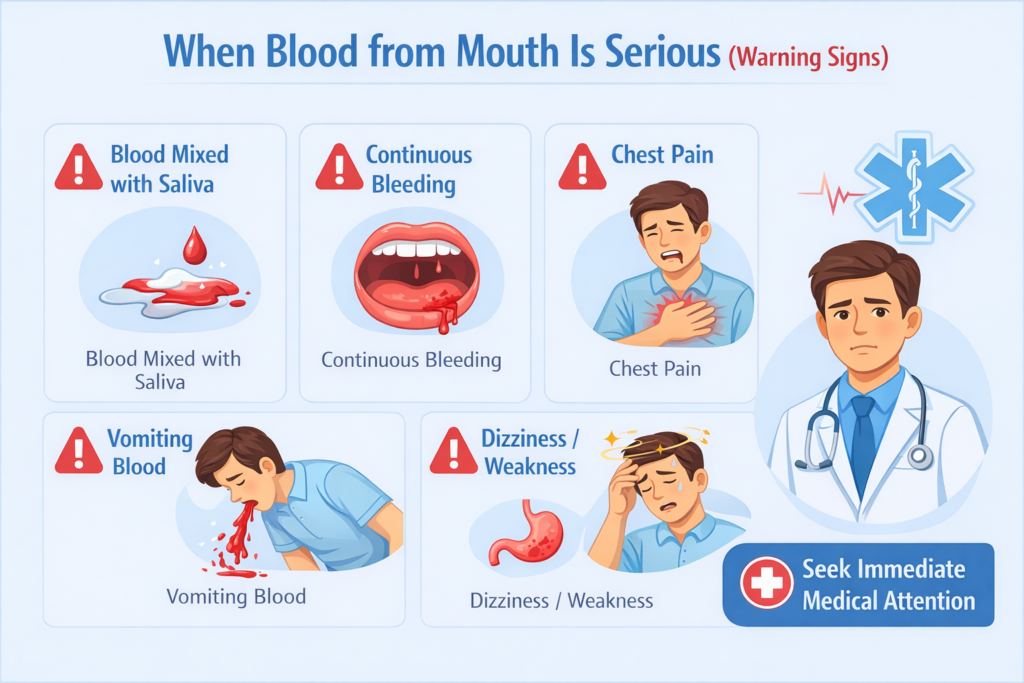
Seek immediate medical care if you experience:
Difficulty breathing or choking
Continuous bleeding lasting more than 24 hours
Swelling of the neck or throat
Large amounts of blood while spitting or coughing
Dizziness, fainting, or weakness
Small amounts of bleeding related to gums or teeth can usually be treated by a dentist, but severe symptoms should never be ignored.
A dentist or doctor may:
Examine your mouth and gums
Check for infections or injuries
Take dental X-rays if required
Review your medical history and medications
Accurate diagnosis ensures proper treatment.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
Professional dental cleaning for gum disease
Correct brushing and flossing techniques
Treatment for tooth infection (medication or root canal)
Nutritional supplements if deficiencies exist
Medical referral if bleeding is not dental-related
You can reduce the risk by:
Brushing twice daily with a soft toothbrush
Flossing gently
Using an antiseptic mouthwash
Avoiding tobacco products
Maintaining a balanced diet
Visiting your dentist every 6 months
Reducing your intake of acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, soda, coffee, and wine, can protect enamel and help you focus on how to cure sensitive teeth in the long term.
If you do consume acidic items, drinking water afterward can help neutralize the acids and protect your enamel
Blood in the mouth is not always serious. Most cases are caused by gum disease, mouth ulcers, or brushing too hard, but persistent or heavy bleeding could indicate an infection, injury, or underlying medical condition. Always consult a dentist if it continues.
For minor bleeding from gums or mouth injuries:
Rinse with cold water
Apply gentle pressure with a clean gauze
Avoid brushing aggressively
If bleeding doesn’t stop within 15–20 minutes, see a dentist immediately.
Common dental diseases that cause bleeding include:
Gum disease (gingivitis / periodontitis)
Oral infections
Mouth ulcers or trauma
Systemic conditions like blood clotting disorders or vitamin deficiencies can also contribute.
Yes, some oral cancers can cause bleeding, usually along with:
Persistent sores
Swelling or lumps
Pain or difficulty swallowing
Early detection by a dentist is critical for effective treatment.
Mouth bleeding can result from:
Gum disease
Brushing or flossing too hard
Mouth injuries or ulcers
Infections or systemic conditions
Rarely, oral cancers or serious medical conditions